As a parent, it is natural to be concerned about your child’s development. From the moment they are born, you eagerly watch for signs of growth and progress. Every smile, every newly acquired skill is a cause for celebration. However, it is also important to be aware of potential red flags that may indicate a delay in your child’s developmental milestones.
During the first few months of life, infants develop at an incredible pace. They can’t yet speak or move on their own, but they communicate with us through their cries, smiles, and body movements. It is crucial to pay attention to their physical and cognitive developments during this time.
By the time your baby is around 3 months old, they should be able to hold their head up steadily and respond to sounds and voices. If your baby doesn’t seem to react to sounds or shows no interest in faces and voices, it might be a cause for concern. It is always best to consult a pediatrician or a specialist in early intervention if you notice any changes in your baby’s behavior.
As your child grows, so do their developmental milestones. From crawling to walking, from babbling to speaking coherently, each stage is an exciting leap forward. However, there are certain signs that may indicate a developmental delay. For toddlers between the ages of 1 and 2 years old, difficulties in handling toys or objects, inability to follow simple directions, and lack of eye contact can be red flags. It is important for parents to address these concerns and seek support from professionals such as occupational therapists or preschool teachers, who can provide guidance and support.
Between the ages of 2 and 3, children should start to show more independence in their activities. They should be able to move around, climb stairs, and speak in short sentences. If you notice that your child is unable to perform these tasks or struggles with basic motor skills, it is crucial to address these concerns and seek the help of a pediatric therapist or occupational therapist.
For school-age children, developmental milestones go beyond physical abilities. The ability to learn and interact in a classroom setting becomes crucial. If your child has difficulty with reading, handwriting, or social interactions, it is essential to seek support from teachers, school psychologists, or occupational therapists. Early intervention can play a vital role in improving outcomes and helping your child reach their full potential.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Your Child’s Developmental Milestones
- 2 Key Indicators for Developmental Milestones
- 3 Red Flags to Watch for in Child Development
- 4 Importance of Tracking Developmental Milestones
- 5 Specific Developmental Red Flags in Children aged 24 to 36 months
- 6 Early Intervention for Developmental Delays
- 7 Resources and Support for Parents
Understanding Your Child’s Developmental Milestones
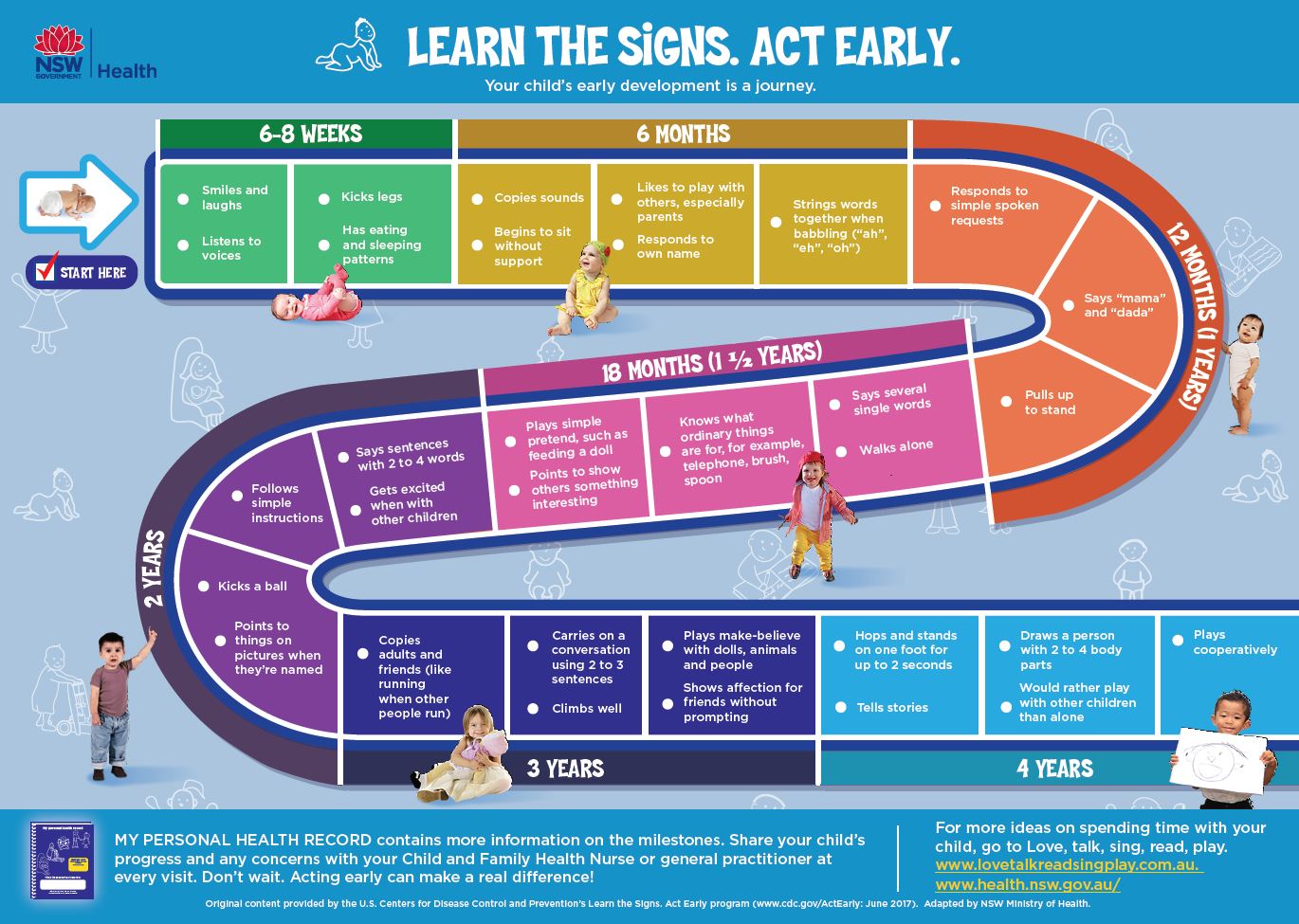
Developmental milestones are key skills and abilities that most children can achieve at certain ages. These milestones are based on the average development of children and can vary from child to child. It is important for parents to be aware of these milestones in order to address any potential developmental delays or concerns.
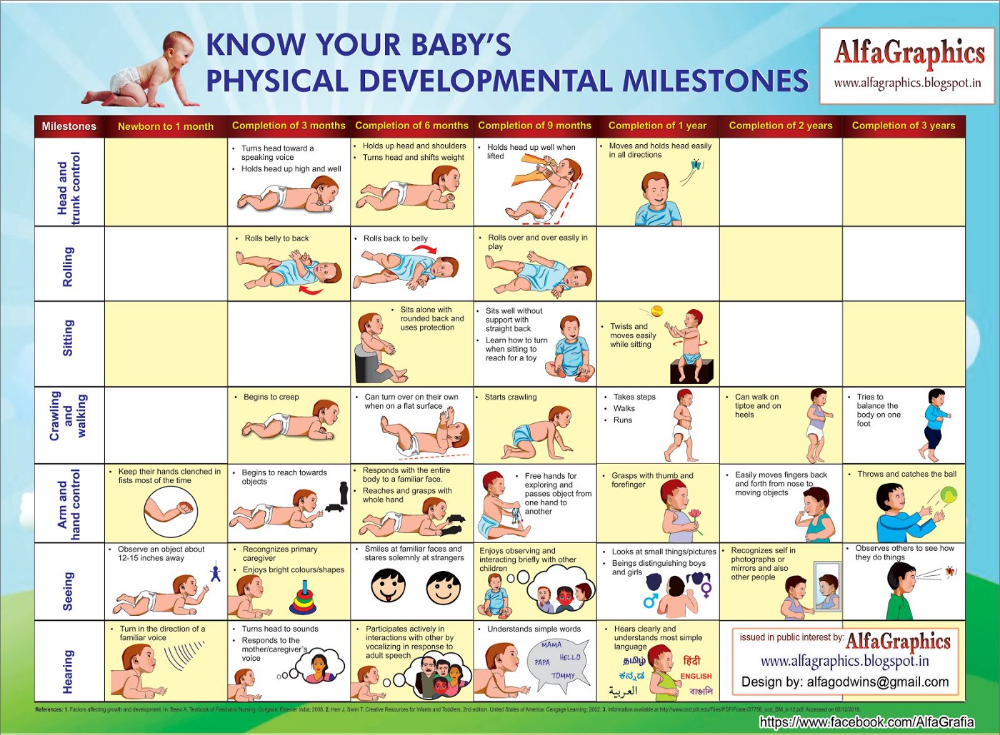
In the first year of life, newborns and infants go through rapid physical and cognitive developments. Within the first month, babies should be able to turn their head and move their arms and legs. By three months, they should be able to smile and coo, showing signs of social interaction. At six months, they should be able to sit up with support and by nine months, they should be able to crawl and pull themselves up to stand.
Between 12 to 24 months, toddlers continue to develop their motor skills and language abilities. They should be able to walk, say a few words, and identify body parts. By the age of two, they should have a vocabulary of about 50 words and begin to form simple sentences. They should also be able to scribble and engage in pretend play.
Preschoolers, between the ages of three to five, show more advanced developments in their language, social, and cognitive abilities. They should be able to speak in complete sentences, follow two to three-step directions, and show empathy towards others. They may also show interest in learning numbers, letters, and shapes.
For school-age children, between the ages of six to 12, developmental milestones include advanced cognitive skills, such as problem-solving and critical thinking. They should be able to read and write independently, and have good handwriting. They may also show interest in hobbies or extracurricular activities.
It is important for parents to understand that reaching these milestones may vary from child to child. However, if a child doesn’t reach these milestones or shows any red flags, it may be necessary to seek intervention from a developmental therapist or occupational therapist. These professionals can address any hidden developmental delays and provide support and strategies to help children catch up with their peers.
In a nutshell, understanding your child’s developmental milestones is crucial in monitoring their growth and addressing any concerns. By keeping track of their developments, parents can ensure that their child is on the right path to achieving optimal outcomes in their physical, cognitive, and social development.
Key Indicators for Developmental Milestones
Developmental milestones are important markers in a child’s growth and progress. As parents, it is crucial to be aware of these milestones and monitor your child for any signs of delay or difficulty in reaching them. Here are some key indicators to watch for:
Newborns (0-1 month):
- Doesn’t respond to loud noises
- Lack of head control
- Difficulty in focusing on faces or objects
- Doesn’t move their arms or legs
Infants (2-12 months):
- Doesn’t smile or show joy
- Doesn’t babble or make sounds
- Doesn’t roll over or sit up without support by 6 months
- Doesn’t crawl or stand with support by 12 months
Toddlers (1-3 years):
- Lack of speech or spoken words
- Doesn’t respond to their name
- Difficulty in following simple instructions
- Doesn’t point or gesture to objects
Preschoolers (3-5 years):
- Difficulty handling toys or objects
- Poor coordination and balance
- Cannot draw simple shapes or copy lines
- Struggles with using utensils or dressing independently
School-age children (6-12 years):
- Difficulty with handwriting and fine motor skills
- Problems with balance and coordination
- Unable to follow multi-step instructions
- Doesn’t engage in age-appropriate play or social interactions
Key Takeaways:
Watching for these key indicators can help parents identify potential developmental delays and seek early intervention if needed. If you notice any red flags or concerns in your child’s development, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional or therapist for support. Remember, addressing developmental milestones early can make a significant difference in a child’s outcomes. Stay proactive and give your child the care and support they need to thrive!
Red Flags to Watch for in Child Development
When it comes to monitoring your child’s development, it’s important to be aware of any red flags indicating potential delays or issues. Early intervention and support can be crucial in addressing developmental concerns and ensuring positive outcomes. Here are some red flags to watch for in child development:
1. Delayed Milestones
Children develop at their own pace, but if your child is significantly lagging behind their peers in reaching milestones such as sitting up, crawling, walking, or talking, it could be a cause for concern.
2. Lack of Muscle Tone
If you notice that your baby’s muscles seem overly floppy or stiff, it may be a sign of potential motor skill delays. Occupational therapists can provide support and guidance to help improve muscle tone and development.
3. Poor Handwriting
For school-age children, messy or illegible handwriting can be a sign of fine motor skill issues. If your child struggles with holding a pencil or forming letters properly, it may be worth seeking evaluation and support from an occupational therapist.
4. Trouble Sleeping
If your child consistently has difficulty falling or staying asleep, it could be a sign of an underlying developmental issue or sleep disorder. Addressing sleep problems can have a significant impact on overall development and well-being.
5. Limited Social Interaction
If your child is not interested in engaging with others, doesn’t respond to their name, or avoids eye contact, it might be worth exploring potential social and communication delays that could benefit from early intervention.
6. Sensory Sensitivities
If your child is overly sensitive to certain textures, sounds, or smells, or if they seek out certain sensory experiences excessively, it could indicate sensory processing issues that would benefit from the support of an occupational therapist.
In a nutshell, it’s important for parents to be vigilant and proactive in monitoring their child’s development. If you notice any of these red flags, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional, therapist, or early childhood specialist for guidance and support. Remember, early intervention is key to addressing developmental concerns and helping children reach their full potential.
Importance of Tracking Developmental Milestones
Tracking your child’s developmental milestones is essential for ensuring their overall growth and well-being. By monitoring their progress, you can identify any potential delays or concerns and seek appropriate intervention if needed. Here’s why tracking developmental milestones matters:
- Early identification of delays: Tracking milestones allows parents and caregivers to identify any developmental delays early on. For example, if a newborn doesn’t turn their head or a 3-month-old doesn’t smile, it could indicate a potential issue that needs to be addressed.
- Support for physical development: Developmental milestones provide a guideline for physical development. For instance, within the first 6 months, infants should start to roll over, sit up, and eventually crawl. By tracking these milestones, parents can support their baby’s physical growth and address any concerns that arise.
- Role in language development: Milestones also play a vital role in language development. From cooing and babbling to speaking their first words, milestones help parents understand what to expect and how to support their child’s language skills.
- Indicator of cognitive abilities: Developmental milestones serve as indicators of cognitive abilities. For example, by 12 months, a toddler should be able to recognize and point at familiar objects. Tracking these milestones can help identify any potential cognitive delays and address them accordingly.
- Identify red flags: Monitoring milestones helps parents identify red flags or warning signs that may indicate a need for further evaluation or therapy. For example, if a preschooler has difficulty with handwriting or a school-age child struggles with basic motor skills, it could be an indication of an underlying developmental issue.
- Address hidden developmental issues: Some developmental issues may not be easily noticeable, especially in newborns. By tracking milestones, parents can detect any hidden developmental issues and seek appropriate interventions or therapies to address them.
- Improve outcomes with early intervention: Timely intervention based on milestone tracking can significantly improve outcomes for children with developmental delays. Occupational therapists and other specialists can provide targeted interventions to help children overcome challenges and reach their full potential.
In a nutshell, tracking your child’s developmental milestones allows you to address any concerns or delays early on, ensuring they receive the support and care they need for optimal development.
Specific Developmental Red Flags in Children aged 24 to 36 months
During the second and third years of life, children undergo significant developmental changes. It is important for parents to observe their child’s milestones during this period to ensure healthy development.
Physical Development
By the age of 24 months, most children can:
- Walk alone steadily
- Turn pages of a book
- Build a tower of six or more blocks
However, if your child:
- Cannot walk or move easily
- Has difficulty handling small objects
- Has muscle tone that is too floppy or too tight
It’s important to check for possible developmental delays and seek early intervention if necessary.
Social and Emotional Development
Between the ages of 24 and 36 months, children start to develop more complex social interactions and emotions. Typical developmental milestones include:
- Showing affection for familiar people
- Engaging in pretend play
- Smiling at themselves in the mirror
However, if your child:
- Shows little interest in other children
- Doesn’t show a range of emotions, such as happiness and sadness
- Doesn’t imitate others’ actions or play make-believe
It’s important to address these red flags and discuss concerns with a pediatrician or a child development specialist.
Speech and Language Development
Between the ages of 2 and 3 years, children typically expand their vocabulary and start using more complex sentences. Developmental expectations include:
- Saying phrases of two to three words
- Following simple directions
- Understanding basic questions
However, if your child:
- Doesn’t speak at least 50 words by 24 months
- Can’t follow simple instructions
- Doesn’t use simple phrases by 36 months
Early intervention with a speech therapist can support their communication goals.
Cognitive Development
By the age of 2 to 3 years, children become more curious and interested in the world around them. They may:
- Sort objects by shape and color
- Build towers of six or more blocks
- Show interest in simple puzzles
However, if your child:
- Doesn’t show an interest in exploring new things
- Has difficulty with basic problem-solving
- Doesn’t show pretend play or imaginative thinking
It’s important for parents to address these developmental concerns and seek appropriate support, such as occupational therapy or educational interventions.
In a nutshell, parents should monitor their child’s development from 24 to 36 months and watch for any red flags. Early intervention plays a crucial role in achieving positive developmental outcomes for children. Parents should trust their instincts and seek professional advice if they have concerns about their child’s development.
Early Intervention for Developmental Delays
Early intervention refers to the process of providing support and care to children who are experiencing developmental delays. Developmental delays can occur in various areas, including physical, cognitive, communication, and social-emotional development.
Why is early intervention important?

Early intervention plays a crucial role in addressing developmental delays and helping children overcome challenges at an early age. It is estimated that 1 in 6 children experiences a developmental delay or disability. By identifying delays and providing intervention as soon as possible, children have a higher chance of achieving positive outcomes.
What are the signs of developmental delays?
Developmental delays can manifest differently in children of different ages. Here are some common signs to watch for:
- Newborn (0-1 month): Difficulty turning the head in both directions, floppy muscle tone, doesn’t focus on faces or follow objects
- Infants (1-12 months): Lack of smiles or joyful expressions, doesn’t make sounds, doesn’t roll over or sit up by 6 months, difficulty handling toys or objects with their hands
- Toddlers (12-36 months): Doesn’t crawl, walk, or move in any direction by 12 months, doesn’t use gestures like pointing or waving, doesn’t speak at least 15 words by 18 months, doesn’t imitate actions or words
- Preschoolers (3-4 years): Difficulty speaking clearly, doesn’t understand or follow simple instructions, cannot use the toilet or dress themselves without assistance
- School-age children (5+ years): Struggles with handwriting, has difficulty with school subjects, has trouble following routines or making friends
What does early intervention involve?
Early intervention typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, where professionals from different fields work together to address the child’s needs. This may include therapists such as occupational, speech, or physical therapists, as well as educators and other specialists.
The specific interventions will depend on the child’s individual needs and may include speech therapy, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other interventions to help them develop essential skills. The goal is to support the child’s overall development and help them reach their maximum potential.
What are the benefits of early intervention?
Early intervention can have a significant impact on a child’s development and future outcomes. Some of the benefits include:
- Improved developmental outcomes
- Better school readiness
- Enhanced social-emotional skills
- Improved language and communication abilities
- Increased independence and self-care skills
In a nutshell, early intervention plays a vital role in identifying and addressing developmental delays in children. By providing support and care early on, we can help children reach their full potential and overcome challenges that may affect their overall development.
Resources and Support for Parents
As a parent, it’s important to have access to resources and support when it comes to your child’s developmental milestones. Here are some key resources that can help:
Early Intervention Programs
Early intervention programs are designed to support children from newborn to three years old who may have developmental delays or disabilities. These programs offer services such as occupational therapy, speech therapy, and physical therapy to help address any areas of concern.
Checklists and Milestone Trackers
Checklists and milestone trackers can be great tools for parents to help track their child’s development. These resources provide a list of developmental milestones for different age groups, so you can easily see if your child is meeting the expected milestones for their age.
Support Groups and Online Communities

Connecting with other parents facing similar challenges can be a valuable source of support. Joining support groups or online communities allows you to share experiences, ask questions, and learn from others who have been through or are going through similar experiences.
Parent Education Programs
Many organizations offer parent education programs that focus on child development. These programs provide parents with the knowledge and skills they need for handling their child’s developmental milestones. Topics covered may include language development, motor skills, sleep patterns, and more.
Professional Guidance
If you have concerns about your child’s development, it’s important to seek professional guidance. Your child’s pediatrician, a developmental pediatrician, or other specialists such as occupational therapists or speech therapists can provide valuable insights and guidance based on their expertise.
In a nutshell, parents play a crucial role in their child’s development. By staying informed, seeking support, and addressing any red flags or concerns early on, parents can help ensure positive outcomes for their children as they grow. Remember, every child develops at their own pace, so it’s important not to compare them to others. Instead, focus on providing a loving and supportive environment where they can thrive.
